
Escherichia coli
O157:H7
Are amphibian tadpoles suitable hosts?
Abstract
Escherichia
coli O157:H7 is a zoonotic pathogen that is
frequently transmitted to humans through contaminated beef and vegetables. Amphibians may function as a reservoir of E.
coli O157:H7 in aquatic environments.
In 2006, we tested whether American bullfrog tadpoles and metamorphs
were suitable hosts of E. coli O157:H7 via controlled
experimental inoculations. Our results
provided the first evidence that American bullfrogs are suitable hosts of this
human pathogen; however, infectivity via controlled experimental inoculation
does not imply individuals can become naturally infected. Thus, we are performing an outdoor mesocosm
experiment that will test if natural infection with E. coli O157:H7 is
possible when bullfrog tadpoles are exposed to contaminated cattle feces. This research will provide an understanding
of whether American bullfrogs function as reservoirs and sources of E.
coli O157:H7 in aquatic environments.
For a more detailed description of the study, please see: http://fwf.ag.utk.edu/mgray/WetlandLab/BThompson.htm.
Collaborators: UT
East Tennessee Research and Education Center, UT Departments of Animal Science
and Forestry, Wildlife and Fisheries, Tennessee Agricultural Experiment Station, UT Center for Wildlife
Health, University of Georgia College of
Veterinary Medicine
Lead Scientists: Dr.
Matthew Gray, Dr.
Alan Mathew, Dr.
Sreekumari Rajeev and Dr.
Debra Miller
Experiment Photos
Mesocosms:

Top row: 300-gal
mesocosms with shade cloth lids, Middle row: 30 mesocosms,
Bottom
row: tadpole addition
Fecal Collection and O157 Slurry:

Top row: fecal
collection and pre-testing for O157, Middle row: fecal slurry,
Bottom
row: E. coli O157 addition and transport to
mesocosm site
Fecal Addition:

Top row: biosafety
supply storage and boot bath, Middle row: O157 slurry addition,
Bottom
row: rinsing and decontaminating containers
Tadpole Collection and Lab Testing:

Top row: netting
tadpoles, Middle row: transporting tadpoles from mesocosm site to lab
and humanely
euthanizing, Bottom row: rinsing tadpoles, packaging, and
decontaminating
More Photos to come!
Recent Outbreaks
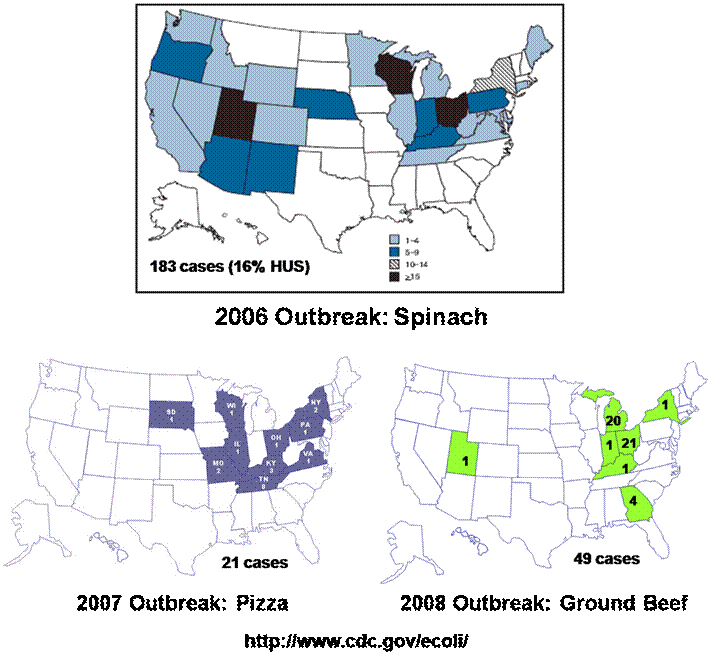
E. coli O157:H7 can cause hemolytic-uremic
syndrome (HUS), which can result in kidney failure and death in humans.
UT Department of Forestry, Wildlife and Fisheries